Building Your Data Quality Roadmap: From Standards to Scorecards
Building Your Data Quality Roadmap: From Standards to Scorecards
If I had a dollar for every time I've heard, "We don't trust our data" or "Our data isn't accurate" or "These reports don't match", I'd be happily retired and certainly wouldn't spend time writing this blog. Issues with data quality are extremely prevalent in a majority of businesses, but in today’s data-driven world, ensuring high-quality data is not just a technical necessity, it’s a strategic advantage. To achieve this, organizations must craft a comprehensive Data Quality Roadmap—one that leads from clear policies and standards all the way to measurable execution outcomes. Let's explore how to create an effective roadmap that ensures your data is trustworthy, consistent, and ready to drive business decisions.
Laying the Foundation: Enterprise Data Management Policy
Building a robust data quality framework starts at the top with an Enterprise Data Management Policy (EDMP). This policy is the "what" of data management—establishing foundational principles that guide how data should be handled throughout the organization. It serves as the cornerstone of all data quality initiatives, ensuring alignment between data management practices and strategic business goals. Without a clear policy, organizations often struggle with quality, compliance, and operational consistency.
Setting the Standards: Data Management and Governance (DM&G)
Once a solid EDMP is in place, the next step is to establish Data Management and Governance Standards. These standards are the "specifications" that outline the requirements for data management, including quality. They provide detailed guidelines to promote consistency, accuracy, and interoperability across data domains. Think of these standards as the objectives that outline the desired quality and consistency of data, serving as benchmarks for an organization to strive for.
Execution Strategies: Bringing Data Quality Standards to Life
With policies and data quality standards defined, the focus turns to the "how" of data quality management. Execution Strategies outline the processes, tools, and technologies needed to adhere to the standards. They are critical for translating high-level principles into day-to-day activities, allowing organizations to manage data quality consistently while adapting to changing needs. These strategies pave the way for data quality practices, ensuring scalability and continuous improvement.
Components of Data Quality Standards
Data Quality Concepts
These are the core concepts, or types of data quality, that ensure data is fit for purpose:
Accuracy: Data should be sufficiently accurate for its intended purposes. Accuracy is most likely to be secured if data is captured as close to the point of activity as possible. Data should be captured once only, although it may have multiple uses. The importance of the uses for the data must be balanced with the costs and effort of collection. Where compromises must be made on accuracy, the limitations of the data should be clear.
Consistency: Data should remain consistent across different data domains and maintain uniformity and coherence.
Reliability: Data should reflect stable and consistent data collection processes across collection points and over time. Users of the data should be confident that improvements reflect real changes rather than variations in data collection approaches or methods.
Timeliness: Data should be captured as quickly as possible after the event or activity and must be available for the intended use within a reasonable time.
Completeness: Data requirements should be clearly specified based on the information needs of the body and data collection processes matched to these requirements. Monitoring missing, incomplete, or invalid records can provide an indication of data quality and can also point to problems in the recording of certain data items.
Pillars of Quality
Key definitions for three major components of overall quality efforts:
Metadata: Metadata is “data about data”. It provides detailed and contextual information about the content, format, structure, and origin of data. Metadata is a critical component of data quality standards as it improves data understanding, documents data ownership and usage, identifies critical data elements, and provides information to enable the tracking and assessment of data quality over time.
Data Lineage: Data lineage refers to the life cycle of data, tracing its flow from origin through various transformations and uses, to its final form(s) or destination(s). Data lineage is often recorded in a visual diagram format and is critical for transparency in data usage, error tracing and resolution, and providing the ability to conduct impact analysis on data quality issues.
Data Quality: Data quality is a measure of the condition of data, assessed by quality the quality concepts accuracy, consistency, reliability, timeliness, and completeness. Having data quality measures are critical to provide clear, measurable targets for improving data quality, managing data quality across the data lifecycle, and ensure the successful integration of data into business processes.
Data Element Concepts
Essential building blocks for structuring and managing quality data:
Critical Data Elements (CDEs): Critical Data Elements are data points that are essential to an organization’s core operations, decision-making processes, regulatory requirements, and risk management. Critical Data Elements warrant stricter data governance practices and quality measures. Both Entities and Attributes can be Critical Data Elements.
Non-Critical Data Elements: Non-Critical Data Elements are all data points that do not meet the criteria to be considered Critical Data Elements.
Entities: A data entity represents a real-world object or concept within an organization’s data ecosystem (e.g. People or Products). Entity definition is crucial for ensuring structural integrity of data, and the mapping of relationships between entities.
Attributes: Attributes provide descriptive details about an entity, characterizing its properties or qualities (e.g. Date of Birth). Attributes are data that is collected about each entity.
Service Level Objectives (SLOs): SLOs are specific, measurable goals related to the quality of data elements. SLOs should be created for each specific data domain and measure the quality of data elements in relation to the concepts of quality. SLOs provide clear quality benchmarking, as well as management and escalation pathways for quality issues.
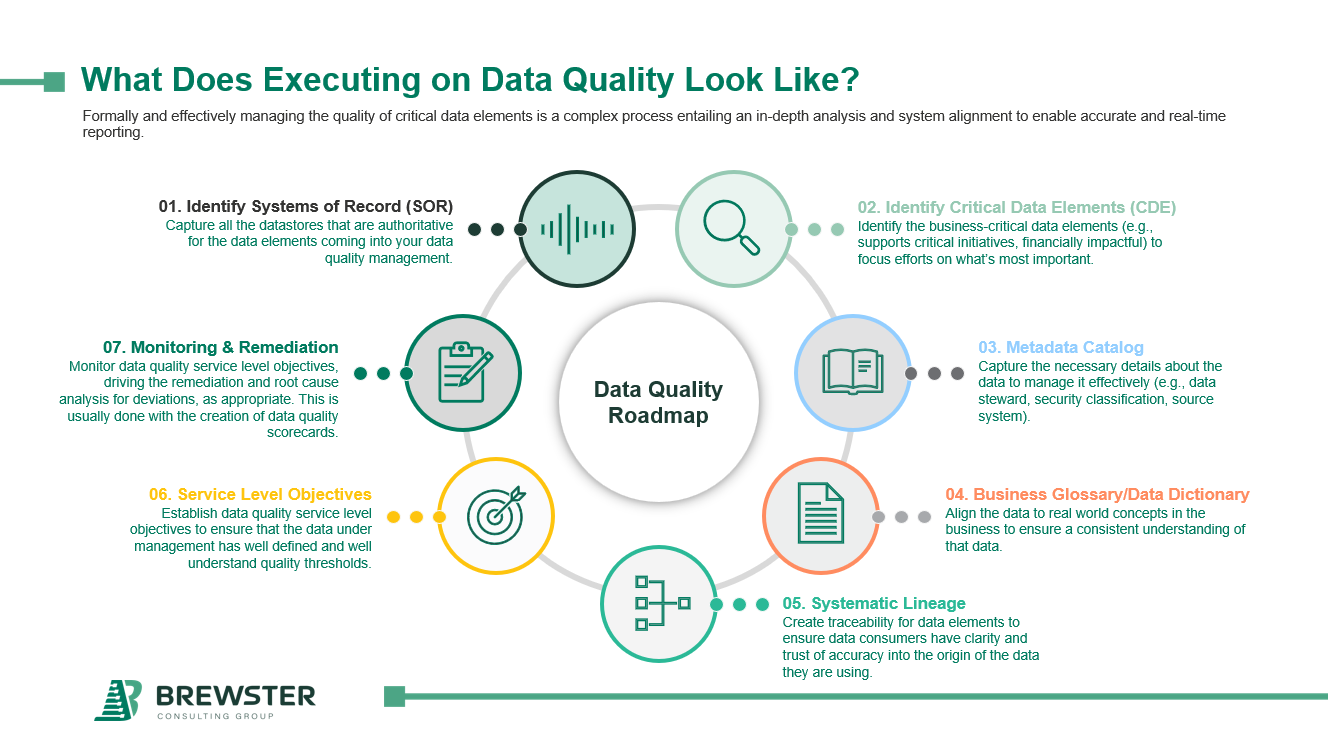
What Does Executing on a Data Quality Roadmap Look Like?
Executing a Data Quality Roadmap is not a one-off project—it's an ongoing process. As seen in our graphic at the top of this page, the steps include:
- Identify Systems of Record (SOR): Capture all the datastores that are authoritative for the data elements coming into your data quality management.
- Identify Critical Data Elements (CDEs): Identify the business-critical data elements (e.g., supports critical initiatives, financially impactful) to focus efforts on what’s most important.
- Metadata Catalog: Capture the necessary details about the data to manage it effectively (e.g., data steward, security classification, source system).
- Business Glossary/Data Dictionary: Align the data to real world concepts in the business to ensure a consistent understanding of that data.
- Systematic Lineage: Create traceability for data elements to ensure data consumers have clarity and trust of accuracy into the origin of the data they are using.
- Service Level Objectives (SLOs): Establish data quality service level objectives to ensure that the data under management has well defined and well understand quality thresholds.
- Monitoring and Remediation: Monitor data quality service level objectives, driving the remediation and root cause analysis for deviations, as appropriate. This is usually done with the creation of data quality scorecards.
Data Quality Scorecards: Measuring Success
An essential tool in this roadmap is the data quality scorecard. These scorecards provide a measurable way to track progress and enforce data quality across the enterprise. By monitoring key metrics such as accuracy, completeness, and timeliness, scorecards not only highlight areas for improvement but also foster accountability among data stakeholders. Effective data quality scorecards give organizations the confidence they need to use their data for strategic decision-making.
Conclusion: Driving Business Value with High-Quality Data
A successful Data Quality Roadmap takes an organization from foundational policies to precise standards and actionable execution. By focusing on core concepts like Critical Data Elements, metadata, data lineage, and using data quality scorecards, organizations can ensure that data remains accurate, reliable, and valuable. This journey is vital for transforming data from a simple resource into a powerful tool that drives business innovation and competitive advantage.
Ready to start your data quality journey? Ensuring data quality isn't just about compliance; it’s about building a foundation for business growth and efficiency. Take the first step today by establishing clear policies and standards, and soon you’ll see the transformative power of high-quality data in action. If you'd like to discuss how you can get started on your data quality journey, please book a meeting with us directly, or reach out via one of our channels.











